Strategies for Managing Hearing Loss in the Workplace
Whether you’re answering phone calls, attending meetings or
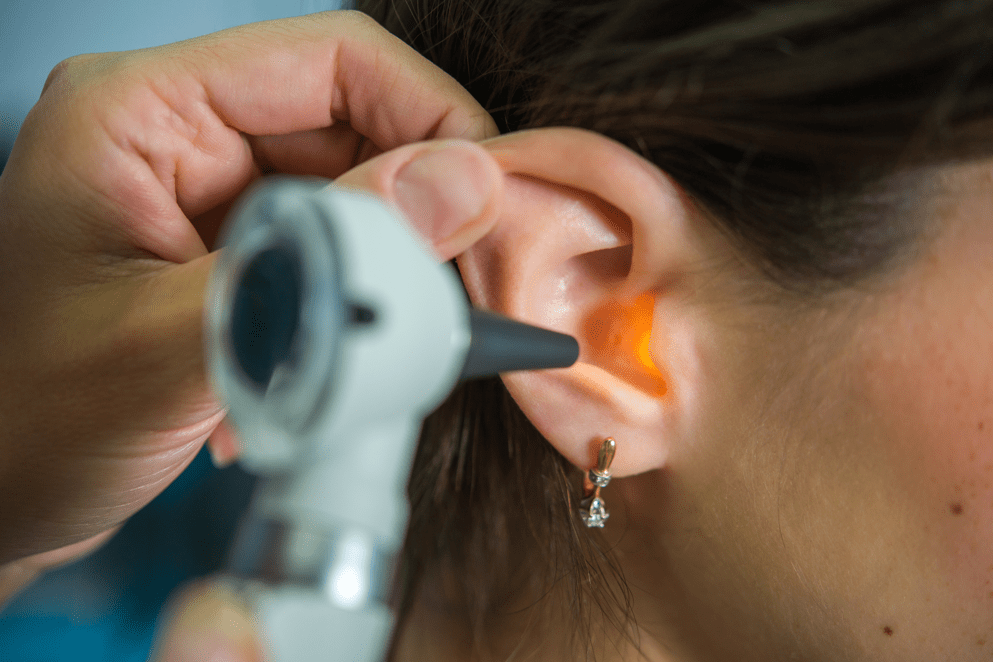

Whether you’re answering phone calls, attending meetings or

Your hearing is an important sense that connects you to the world, yet

Are you curious about how hearing loss might impact your upcoming travel